JsonCons JsonPath Specification
Grammar
jsonpath = root [relative-location]
jsonpath = current-node [relative-location]
relative-location = "." relative-path
relative-location =/ recursive-descent relative-path
relative-location =/ recursive-descent bracket-expression [relative-location]
relative-location =/ parent [relative-location]
relative-path = identifier [relative-location]
relative-path =/ wildcard [relative-location]
bracket-expression = "[" bracketed-element *("," bracketed-element) "]"
bracketed-element = index / slice-expression / single-quoted-string / double-quoted-string
bracketed-element =/ wildcard / filter-expression / jsonpath
root = "$"
current-node = "@"
parent = "^"
identifier = unquoted-string / single-quoted-string / double-quoted-string
unquoted-string = %x30-39 / ; 0-9
%x41-5A / ; A-Z
%x5F / ; _
%x61-7A / ; a-z
%x80-10FFFF ; U+0080 ...
single-quoted-string = single-quote
1*(unescaped-char / double-quote /
escaped-char / escaped-single-quote)
single-quote
double-quoted-string = double-quote
1*(unescaped-char / single-quote /
escaped-char / escaped-double-quote)
double-quote
escaped-single-quote = escape single-quote ; ' single quote U+002c
escaped-double-quote = escape double-quote ; " double quote U+0022
single-quote = %x2c ; Single quote: "'"
double-quote = %x22 ; Double quote: '"'
unescaped-char = %x20-21 / %x23-2b / %x2d-5B / %x5D-10FFFF
escape = %x5C ; Back slash: \
escaped-char = escape (
%x5C / ; \ reverse solidus U+005C
%x2F / ; / solidus U+002F
%x62 / ; b backspace U+0008
%x66 / ; f form feed U+000C
%x6E / ; n line feed U+000A
%x72 / ; r carriage return U+000D
%x74 / ; t tab U+0009
%x75 4HEXDIG ) ; uXXXX U+XXXX
index = integer
slice = [integer] ":" [integer] [ ":" [integer] ]
recursive-descent = ".."
wildcard = "*"
integer = ["-"]1*digit
filter-expression = "?" expression
expression = single-quoted-string
expression =/ json-literal ; any valid JSON value
expression =/ jsonpath
expression =/ unary-expression / binary-expression / regex-expression / paren-expression
paren-expression = "(" expression ")"
unary-expression=unary-operator expression
binary-expression = expression binary-operator expression
regex-expression = expression regex-operator "/" regex "/" [i]
unary-operator = "!" / "-"
binary-operator = "*" / "/" / "%" / "+" / "-" / "&&" / "||" / <" / "<=" / "==" / ">=" / ">" / "!="
regex-operator = "=~"
;
; "regex" represents regular expression characters
function-expression = unquoted-string (
no-args /
one-or-more-args )
no-args = "(" ")"
one-or-more-args = "(" ( function-arg *( "," function-arg ) ) ")"
function-arg = expression
Selectors
After tokenization, a JSONPath string is transformed into a null terminated linked list of selectors. There are ten different kinds of selectors:
Root selector ($)
Current node selector (@)
Parent node selector (^)
Identifier selector
Index selector
Slice selector
Recursive descent selector (..)
Wildcard selector (*)
Union selector
Filter selector
The selectors arranged in a linked list take a JSON value as input and produce a list of JSON values as output. Evaluation proceeds as follows:
The selector at the head of the list will select zero, one or many items from its provided value, and, for each item, evaluate the tail of the list (recursively.) For example, given
and a JSONPath[{"a":"bar"},{"b":"baz"},{"b":"qux"}]
the root selector will select the root and evaluate$.*.b*.b(root), the wildcard selector will select the elements in the root and evaluateb({"a":"bar"}),b({"b":"baz"}), andb({"b":"qux"}).When the tail is null, evaluation stops. The last selector in the list will add its provided value to the output list.
Note that only the last selector adds to the output list.
Consider the JSON document
{"foo":[
{"a":"bar"},
{"b":"baz"},
{"b":"qux"}
]}
and JSONPath
$.foo[*].b
After tokenization, the JSONPath becomes

Evaluation proceeds as follows:
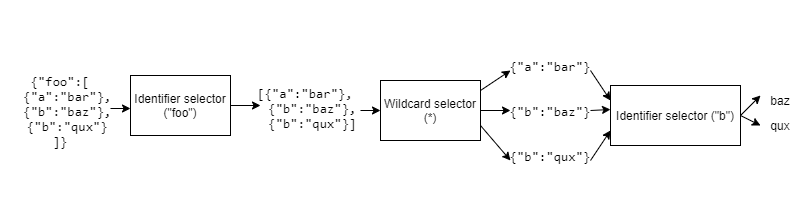
The final result is
["baz","qux"]
Root selector
root = "$"
The symbol "$" represents the root JSON value, the JSON document to be evaluated. The root selector selects this value.
Current node selector
current-node = "@"
The symbol "@" represents the "current node". At the start of an expression,
the current node is the document to be evaluated, and as the expression
is evaluated, it changes to reflect the node currently being processed.
The current node selector selects this value.
Parent selector
parent = "^"
The symbol "^" represents the parent of the current node.
Consider the JSON document
[
{
"author" : "Haruki Murakami",
"title": "A Wild Sheep Chase",
"reviews": [{"rating": 4, "reviewer": "Nan"}]
},
{
"author" : "Sergei Lukyanenko",
"title": "The Night Watch",
"reviews": [{"rating": 5, "reviewer": "Alan"},
{"rating": 3,"reviewer": "Anne"}]
},
{
"author" : "Graham Greene",
"title": "The Comedians",
"reviews": [{"rating": 4, "reviewer": "Lisa"},
{"rating": 5, "reviewer": "Robert"}]
}
]
JsonCons supports the parent selector, ^, borrowed from JSONPath Plus,
that allows you to select book objects based on criteria applied to descendent values.
| Query | Output paths |
|---|---|
$[*]reviews[?(@.rating == 5)] |
"$[1]['reviews'][0]" |
| "$[2]['reviews'][1]" | |
$[*]reviews[?(@.rating == 5)]^ |
"$[1]['reviews']" |
| "$[2]['reviews']" | |
$[*]reviews[?(@.rating == 5)]^^ |
"$[1]" |
| "$[2]" |
The JSONPath expression
$[*].reviews[?(@.rating == 5)]^^
selects all the book objects that have ratings of 5:
[
{
"author": "Sergei Lukyanenko",
"reviews": [
{
"rating": 5,
"reviewer": "Alan"
},
{
"rating": 3,
"reviewer": "Anne"
}
],
"title": "The Night Watch"
},
{
"author": "Graham Greene",
"reviews": [
{
"rating": 4,
"reviewer": "Lisa"
},
{
"rating": 5,
"reviewer": "Robert"
}
],
"title": "The Comedians"
}
]
Identifier selector
identifier = unquoted-string / single-quoted-string / double-quoted-string
unquoted-string = %x30-39 / ; 0-9
%x41-5A / ; A-Z
%x5F / ; _
%x61-7A / ; a-z
%x80-10FFFF ; U+0080 ...
single-quoted-string = single-quote
1*(unescaped-char / double-quote /
escaped-char / escaped-single-quote)
single-quote
double-quoted-string = double-quote
1*(unescaped-char / single-quote /
escaped-char / escaped-double-quote)
double-quote
escaped-single-quote = escape single-quote ; ' single quote U+002c
escaped-double-quote = escape double-quote ; " double quote U+0022
single-quote = %x2c ; Single quote: "'"
double-quote = %x22 ; Double quote: '"'
unescaped-char = %x20-21 / %x23-2b / %x2d-5B / %x5D-10FFFF
escape = %x5C ; Back slash: \
escaped-char = escape (
%x5C / ; \ reverse solidus U+005C
%x2F / ; / solidus U+002F
%x62 / ; b backspace U+0008
%x66 / ; f form feed U+000C
%x6E / ; n line feed U+000A
%x72 / ; r carriage return U+000D
%x74 / ; t tab U+0009
%x75 4HEXDIG ) ; uXXXX U+XXXX
An identifier selector selects zero or one values from a JSON value, depending on whether it is an object that has a member with a corresponding name.
Index selector
index = integer
An index selector selects zero or one values from a JSON value, depending on whether it is an array with an element at a corresponding index. Indexing is zero-based. A negative index indicates that indexing is relative to the end of the array.
Slice selector
slice = [integer] ":" [integer] [ ":" [integer] ]
JsonCons jsonpath slices have the same semantics as Python slices
The syntax for a slice is
[start:stop:step]
Each component is optional.
If
startis omitted, it defaults to0ifstepis positive, or the end of the array ifstepis negative.If
stopis omitted, it defaults to the length of the array ifstepis positive, or the beginning of the array ifstepis negative.If
stepis omitted, it defaults to1.
| Slice expression | Description |
|---|---|
[start:stop] |
Items start through stop-1 |
[start:] |
Items start to the end of the array |
[:stop] |
Items from the beginning of the array through stop-1 |
[:] |
All items |
[start:stop:step] |
Items start up to but not including stop, by step |
A component start, stop, or step may be a negative number.
| Example | Description |
|---|---|
| $[-1] | Last item |
| $[-2:] | Last two items |
| $[:-2] | All items except the last two |
| $[::-1] | All items, reversed |
| $[1::-1] | First two items, reversed |
| $[:-3:-1] | Last two items, reversed |
| $[-3::-1] | All items except the last two, reversed |
Recursive descent selector
recursive-descent = ".."
The recursive descent selector performs a select operation on a provided JSON value as follows:
If its tail is null, it adds the value to the result list, and exits. Otherwise, it continues as below.
If the provided value is a JSON array, it first provides the value to its tail, and then iterates over each item in the array, recursively performing the select operation on each item.
If the provided value is a JSON object, it first provides the value to its tail, and then iterates over each property in the object, recursively performing the select operation on each property's value.
Consider the JSON document
{"foo":[
{"a":"bar"},
{"b":"baz"},
{"b":"qux"}
]}
and JSONPath
$..b
After tokenization, the JSONPath becomes

Evaluation proceeds as follows:
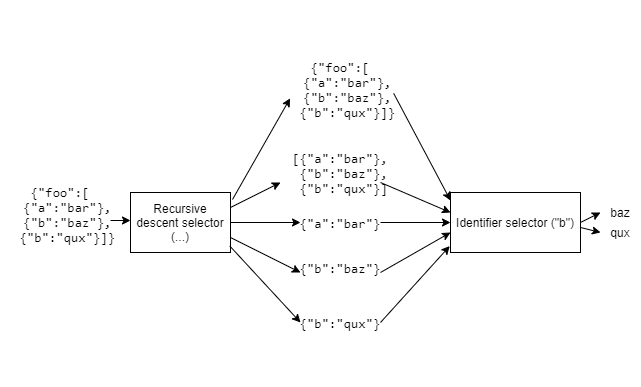
The final result is
["baz","qux"]
Wildcard selector
wildcard = "*"
The wildcard selector can select multiple items. If provided with an array, it will select all the array's elements, and if provided with an object, it will select the value part of all the object's name-value pairs.
Unions
bracket-expression = "[" bracketed-element *("," bracketed-element) "]"
bracketed-element = index / slice-expression / single-quoted-string / double-quoted-string
bracketed-element =/ wildcard / filter-expression / jsonpath
In JsonCons, a JSONPath union element can be
- an index or slice expression
- a single quoted name
- a double quoted name
- a filter
- a wildcard, i.e.
* - a path relative to the root of the JSON document (begins with
$) - a path relative to the current value being processed (begins with
@)
To illustrate, the path expression below selects the first and second titles, the last, and the third from Stefan Goessner's store:
"$.store.book[0:2,-1,?(@.author=='Herman Melville')].title"
Filter selector
filter-expression = "?" expression
expression = single-quoted-string
expression =/ json-literal ; any valid JSON value
expression =/ jsonpath
expression =/ unary-expression / binary-expression / regex-expression / paren-expression
paren-expression = "(" expression ")"
unary-expression=unary-operator expression
binary-expression = expression binary-operator expression
regex-expression = expression regex-operator "/" regex "/" [i]
unary-operator = "!" / "-"
binary-operator = "*" / "/" / "%" / "+" / "-" / "&&" / "||" / <" / "<=" / "==" / ">=" / ">" / "!="
regex-operator = "=~"
;
; "regex" represents regular expression characters
function-expression = unquoted-string (
no-args /
one-or-more-args )
no-args = "(" ")"
one-or-more-args = "(" ( function-arg *( "," function-arg ) ) ")"
function-arg = expression
JSONPath uses filter expressions [?<expr>] to restrict the set of nodes
returned by a path, e.g. $..book[?(@.price<10)] returns the books with
prices less than 10. Filter expressions are applied to each element in a
JSON array or each member in a JSON object. The symbol @ represents the
value currently being processed. An expression evaluates to true or false,
if true, the array element, or value part of an object member, is selected.
An expression is considered false if it evaluates to any of the following values:
- empty array: [],
- empty object: {},
- empty string: "",
- false,
- null.
It is considered true if it is not false.
Filter Expressions
True and False Values
A false value is any value on this list:
- empty array: [],
- empty object: {},
- empty string: "",
- false,
- null.
A true value is any value that is not false
Operands
The operands in an expression may be a jsonpath
jsonpath = "$" [relative-location]
jsonpath = "@" [relative-location]
a single-quoted-string, or a json-literal.
For example, given a JSON document
[[1, 2, 3], [1], [2, 3], "1", "2"]
the four queries below are all valid
$[?@ == '2']
$[?@ == [1,2,3]]
$[?@[0:1]==[1]]
$[?$[2] == [2,3]]
and produce the results
["2"]
[[1,2, 3]]
[[1, 2, 3], [1]]
[[1, 2, 3], [1], [2, 3], "1", "2"]
In an expression, a jsonpath is not evaluated as a
collection of matching JSON values, but rather, as a single JSON value.
The slice, recursive descent, wildcard, union and filter selectors,
which can evaluate to zero, one, or many items, are wrapped
in a Json array. The others - root, current node, parent node,
identifier, and index selectors - evaluate to a single value if
matched, otherwise a null value.
Operator Precedence
The table below lists operators in descending order of precedence (upper rows bind tighter than lower ones.)
| Precedence | Operator | Associativity |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | ! unary - |
Right |
| 7 | =~ |
Left |
| 6 | * / % |
Left |
| 5 | + - |
Left |
| 4 | < > <= >= |
Left |
| 3 | == != |
Left |
| 2 | && |
Left |
| 1 | || |
Left |
The precedence rules may be overriden with explicit parentheses, e.g. (a || b) && c.
Or Expression
or-expression = expression "||" expression
If both left and right sides are null, the or-expression evaluates to null. Otherwise, if the left side evaluates to true, it will evaluate to its left side, and if the left side evaluates to false, it will evaluate to its right side.
And Expression
and-expression = expression "&&" expression
If the left side evaluates to true, then the and-expression evaluates to the right side, otherwise it evaluates to the left side.
Not Expression
not-expression = "!" expression
If an expression evaluates to true, a not-expression will evaluate to false. Conversely if an expression evaluates to false, a not-expression will evaluate to true;
Unary Minus Expression
unary-minus-expression = -expression
The - (unary minus) operator negates the value of the expression. It is only valid if the expression evaluates to a number.
Example
JSON Document:
[{"key": 0}, {"key": 42}, {"key": -1}, {"key": 41}, {"key": 43}, {"key": 42.0001}, {"key": 41.9999}, {"key": 100}, {"some": "value"}]
JSONPath:
$[?-@.key > -42]
Result:
[{"key": 0}, {"key": -1}, {"key": 41}, {"key": 41.9999}]
Functions
abs
number abs(number value)
Returns the absolute value of a number.
It is a type error if the provided argument is not a number.
Examples
avg
number|null avg(array[number] value)
Returns the average of the items in an array of numbers, or null if the array is empty
It is a type error if
the provided value is not an array
the array contains items that are not numbers
Examples
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.Json;
using JsonCons.JsonPath;
namespace JsonCons.Examples
{
public static class JsonPathExamples
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string jsonString = @"
{
""books"":
[
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""A Wild Sheep Chase"",
""author"" : ""Haruki Murakami"",
""price"" : 22.72
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Night Watch"",
""author"" : ""Sergei Lukyanenko"",
""price"" : 23.58
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Comedians"",
""author"" : ""Graham Greene"",
""price"" : 21.99
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""author"": ""J. R. R. Tolkien"",
""title"": ""The Lord of the Rings""
}
]
}
";
using (JsonDocument doc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString))
{
IList<JsonElement> results = JsonPath.Select(doc.RootElement, @"$.books[?(@.price > avg($.books[*].price))].title");
foreach (var value in results)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
"The Night Watch"
ceil
integer ceil(number value)
Returns the smallest integer value not less than the provided number.
It is a type error if the provided argument is not a number.
Examples
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.Json;
using JsonCons.JsonPath;
namespace JsonCons.Examples
{
public static class JsonPathExamples
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string jsonString = @"
{
""books"":
[
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""A Wild Sheep Chase"",
""author"" : ""Haruki Murakami"",
""price"" : 22.72
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Night Watch"",
""author"" : ""Sergei Lukyanenko"",
""price"" : 23.58
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Comedians"",
""author"" : ""Graham Greene"",
""price"" : 21.99
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""author"": ""J. R. R. Tolkien"",
""title"": ""The Lord of the Rings""
}
]
}
";
using (JsonDocument doc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString))
{
IList<JsonElement> results = JsonPath.Select(doc.RootElement, @"$.books[?(ceil(@.price*10) == 236)]");
foreach (var value in results)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
{
"category": "fiction",
"title" : "The Night Watch",
"author" : "Sergei Lukyanenko",
"price" : 23.58
}
contains
boolean contains(array|string source, any search)
If source is an array, returns true if the array contains an item that is equal to the search value, false otherwise.
If source is a string, returns true if the string contains a substring that is equal to the search value, false otherwise.
It is a type error if
the provided source is not an array or string, or
the provided source is a string but the provided search value is not a string.
Examples
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.Json;
using JsonCons.JsonPath;
namespace JsonCons.Examples
{
public static class JsonPathExamples
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string jsonString = @"
{
""books"":
[
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""A Wild Sheep Chase"",
""author"" : ""Haruki Murakami"",
""price"" : 22.72
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Night Watch"",
""author"" : ""Sergei Lukyanenko"",
""price"" : 23.58
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Comedians"",
""author"" : ""Graham Greene"",
""price"" : 21.99
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""author"": ""J. R. R. Tolkien"",
""title"": ""The Lord of the Rings""
}
]
}
";
using (JsonDocument doc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString))
{
IList<JsonElement> results = JsonPath.Select(doc.RootElement, @"$.books[?(!contains(keys(@),'price'))]");
foreach (var value in results)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings"
}
ends_with
boolean ends_with(string source, string suffix)
Returns true if the source string ends with the suffix string, otherwise false.
It is a type error if
the provided source is not a string, or
the provided suffix is not a string
Examples
floor
integer floor(number value)
Returns the largest integer value not greater than the given number.
It is a type error if the provided argument is not a number.
Examples
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.Json;
using JsonCons.JsonPath;
namespace JsonCons.Examples
{
public static class JsonPathExamples
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string jsonString = @"
{
""books"":
[
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""A Wild Sheep Chase"",
""author"" : ""Haruki Murakami"",
""price"" : 22.72
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Night Watch"",
""author"" : ""Sergei Lukyanenko"",
""price"" : 23.58
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Comedians"",
""author"" : ""Graham Greene"",
""price"" : 21.99
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""author"": ""J. R. R. Tolkien"",
""title"": ""The Lord of the Rings""
}
]
}
";
using (JsonDocument doc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString))
{
IList<JsonElement> results = JsonPath.Select(doc.RootElement, @"$.books[?(floor(@.price*10) == 235)]");
foreach (var value in results)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
{
"category": "fiction",
"title" : "A Wild Sheep Chase",
"author" : "Haruki Murakami",
"price" : 22.72
}
keys
array[string] keys(object value)
Returns an array of keys in the object.
It is a type error if the provided argument is not an object.
Example
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.Json;
using JsonCons.JsonPath;
namespace JsonCons.Examples
{
public static class JsonPathExamples
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string jsonString = @"
{
""books"":
[
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""A Wild Sheep Chase"",
""author"" : ""Haruki Murakami"",
""price"" : 22.72
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Night Watch"",
""author"" : ""Sergei Lukyanenko"",
""price"" : 23.58
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Comedians"",
""author"" : ""Graham Greene"",
""price"" : 21.99
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""author"": ""J. R. R. Tolkien"",
""title"": ""The Lord of the Rings""
}
]
}
";
using (JsonDocument doc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString))
{
IList<JsonElement> results = JsonPath.Select(doc.RootElement, @"$.books[?(tokenize(@.author,'\\s+')[-1] == 'Tolkien')]");
foreach (var value in results)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings"
}
length
integer|null length(array|object|string value)
Returns the length of an array, object or string.
If array, returns the number of items in the array If object, returns the number of key-value pairs in the object If string, returns the number of codepoints in the string Otherwise, returns null.
Examples
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.Json;
using JsonCons.JsonPath;
namespace JsonCons.Examples
{
public static class JsonPathExamples
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string jsonString = @"
{
""books"":
[
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""A Wild Sheep Chase"",
""author"" : ""Haruki Murakami"",
""price"" : 22.72
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Night Watch"",
""author"" : ""Sergei Lukyanenko"",
""price"" : 23.58
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Comedians"",
""author"" : ""Graham Greene"",
""price"" : 21.99
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""author"": ""J. R. R. Tolkien"",
""title"": ""The Lord of the Rings""
}
]
}
";
using (JsonDocument doc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString))
{
IList<JsonElement> results3 = JsonPath.Select(doc.RootElement, @"$.books[?(@.price > sum($.books[*].price)/length($.books[*].price))].title");
foreach (var value in results3)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
"The Night Watch"
max
number|string|null max(array[number]|array[string] value)
Returns the highest number found in an array of numbers, or the highest string in an array of strings, or null if the array is empty.
It is a type error if
the provided value is not an array
the array contains items that are not all numbers or all strings
Examples
min
number|string|null min(array[number]|array[string] value)
Returns the lowest number found in an array of numbers, or the lowest string in an array of strings, or null if the array is empty
It is a type error if
the provided value is not an array
the array contains items that are not all numbers or all strings
Examples
prod
number|null avg(array[number] value)
Returns the product of the items in an array of numbers, or null if the array is empty.
It is a type error if
the provided value is not an array
the array contains items that are not numbers
Examples
starts_with
boolean starts_with(string source, string prefix)
Returns true if the source string starts with the prefix string, otherwise false.
It is a type error if
- the provided source is not a string, or
- the provided prefix is not a string
Examples
sum
number sum(array[number] value)
Returns the sum of the items in an array of numbers.
Returns 0 if the array is empty.
It is a type error if any item in the array is not a number.
Examples
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.Json;
using JsonCons.JsonPath;
namespace JsonCons.Examples
{
public static class JsonPathExamples
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string jsonString = @"
{
""books"":
[
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""A Wild Sheep Chase"",
""author"" : ""Haruki Murakami"",
""price"" : 22.72
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Night Watch"",
""author"" : ""Sergei Lukyanenko"",
""price"" : 23.58
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Comedians"",
""author"" : ""Graham Greene"",
""price"" : 21.99
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""author"": ""J. R. R. Tolkien"",
""title"": ""The Lord of the Rings""
}
]
}
";
using (JsonDocument doc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString))
{
IList<JsonElement> results3 = JsonPath.Select(doc.RootElement, @"$.books[?(@.price > sum($.books[*].price)/length($.books[*].price))].title");
foreach (var value in results3)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
"The Night Watch"
to_number
number to_number(string|number value)
If string, returns the parsed number. If number, returns the passed in value.
It is a type error if
the provided value is not a string or number
the string cannot be parsed as a number
Examples
tokenize
array[string] tokenize(string source, string pattern)
Returns an array of strings formed by splitting the source string into an array of strings, separated by substrings that match the given regular expression pattern.
It is a type error if either argument is not a string.
Example
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text.Json;
using JsonCons.JsonPath;
namespace JsonCons.Examples
{
public static class JsonPathExamples
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string jsonString = @"
{
""books"":
[
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""A Wild Sheep Chase"",
""author"" : ""Haruki Murakami"",
""price"" : 22.72
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Night Watch"",
""author"" : ""Sergei Lukyanenko"",
""price"" : 23.58
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""title"" : ""The Comedians"",
""author"" : ""Graham Greene"",
""price"" : 21.99
},
{
""category"": ""fiction"",
""author"": ""J. R. R. Tolkien"",
""title"": ""The Lord of the Rings""
}
]
}
";
using (JsonDocument doc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString))
{
IList<JsonElement> results = JsonPath.Select(doc.RootElement, @"$.books[?(tokenize(@.author,'\\s+')[-1] == 'Tolkien')]");
foreach (var value in results)
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
}
}
Output:
{
"category": "fiction",
"author": "J. R. R. Tolkien",
"title": "The Lord of the Rings"
}